Introduction:

1.Steam Methane Reforming (SMR):

2.Partial Oxidation of Hydrocarbons:
3.Electrolysis:
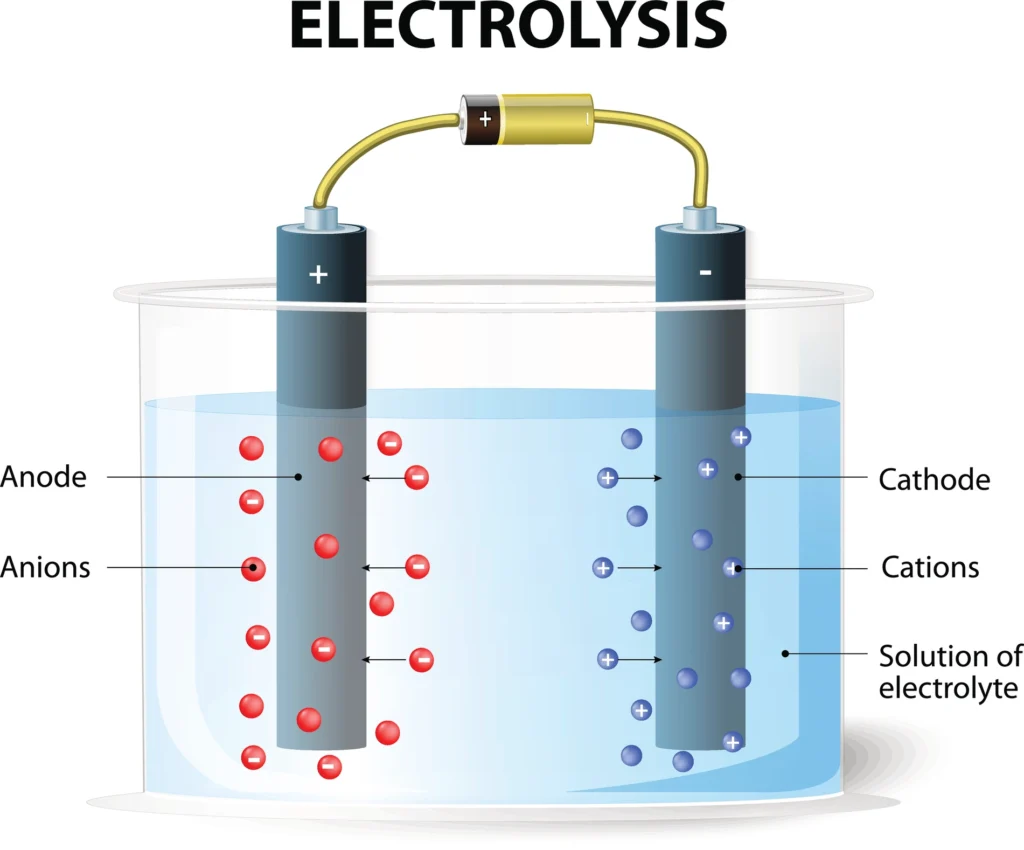
a. Alkaline Electrolysis:

b. PEM Electrolysis:
PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane) electrolysis efficiently splits water into hydrogen and oxygen (2H2O → 2H2 + O2), operating at lower temperatures and pressures than alkaline systems. This results in higher efficiency and faster response times. However, the echnology remains relatively expensive due to the cost of membrane materials like platinum. Despite challenges, PEM electrolyzers hold promise for sustainable hydrogen production, driving advancements towards cost reduction and wider adoption in renewable energy systems.
c. AEM Electrolysis
AEM (Anion Exchange Membrane) electrolysis is a promising method for hydrogen production, operating similarly to PEM electrolysis but using an anion exchange membrane instead. AEM electrolysis offers advantages such as lower cost due to the absence of expensive precious metal catalysts like platinum. It utilizes renewable electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, contributing to the development of sustainable hydrogen production technologies for a greener future.

d. Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell (SOEC):
4.Biological Hydrogen Production:
Biological hydrogen production harnesses the metabolic activities of microorganisms to generate hydrogen gas from organic substrates through fermentation or photosynthesis processes.













